Passing variables
Actions
- The first action builds the application and saves the log output to
logs.txt:
Image loading...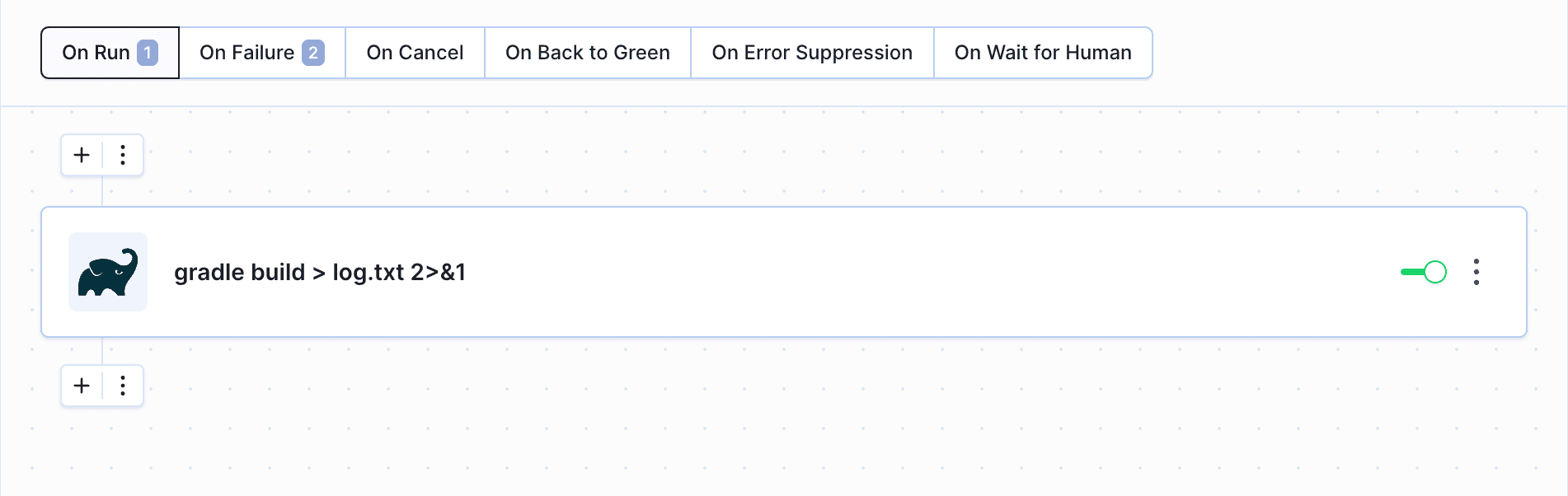
- In case the build fails, the Local Shell action assigns the content of
logs.txtto a variable usingexport LOGS=$(cat log.txt). The logs are then sent to a Slack channel with$LOGSas the message content:
Image loading...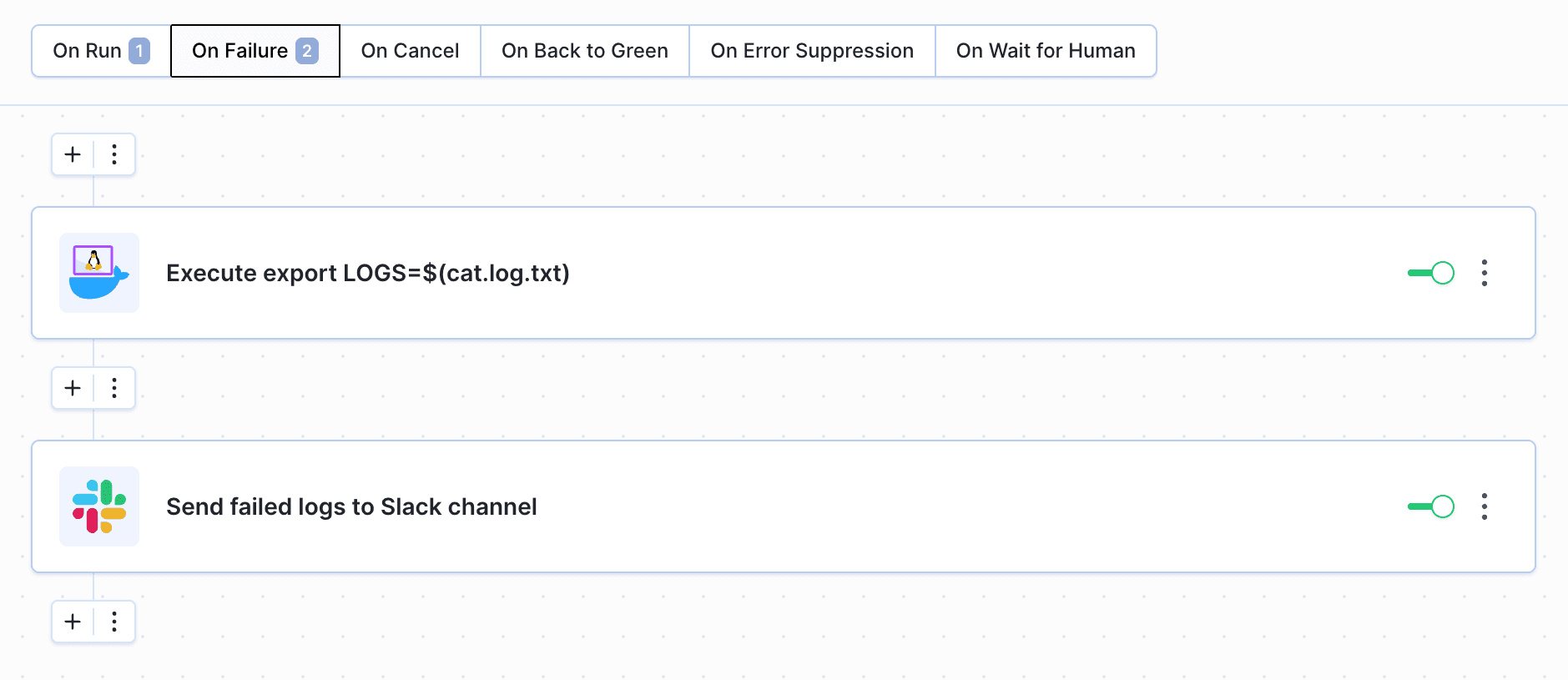
$BUDDY_FAILED_ACTION_LOGS instead of manually exporting the logs to a file.
Pipeline runs
You can pass the values of variables between pipeline runs as well. The values can be saved in one run and then used in another one, e.g. you can set a variable with the version type and increment it in every run.
Pipelines
You can pass a variable between pipelines using the Trigger pipeline action:
- Go to the Variables tab in the action details.
- Define the name of the variable and the value to pass:
Image loading...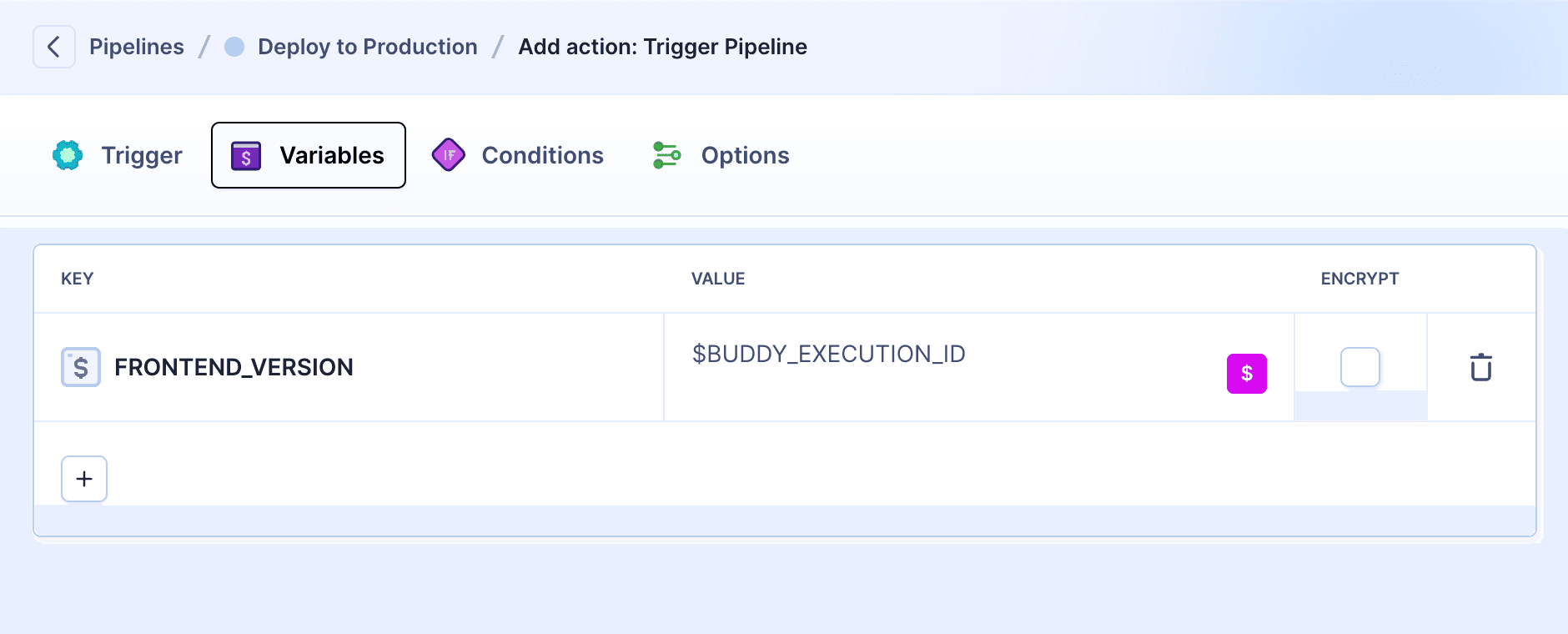
Resetting
To reset settable variables between pipeline runs, you can add an action with a command that will clear the value of the variable (preferably at the beginning or at the end of the pipeline):
bashexport mySettableEnv=$
Image loading...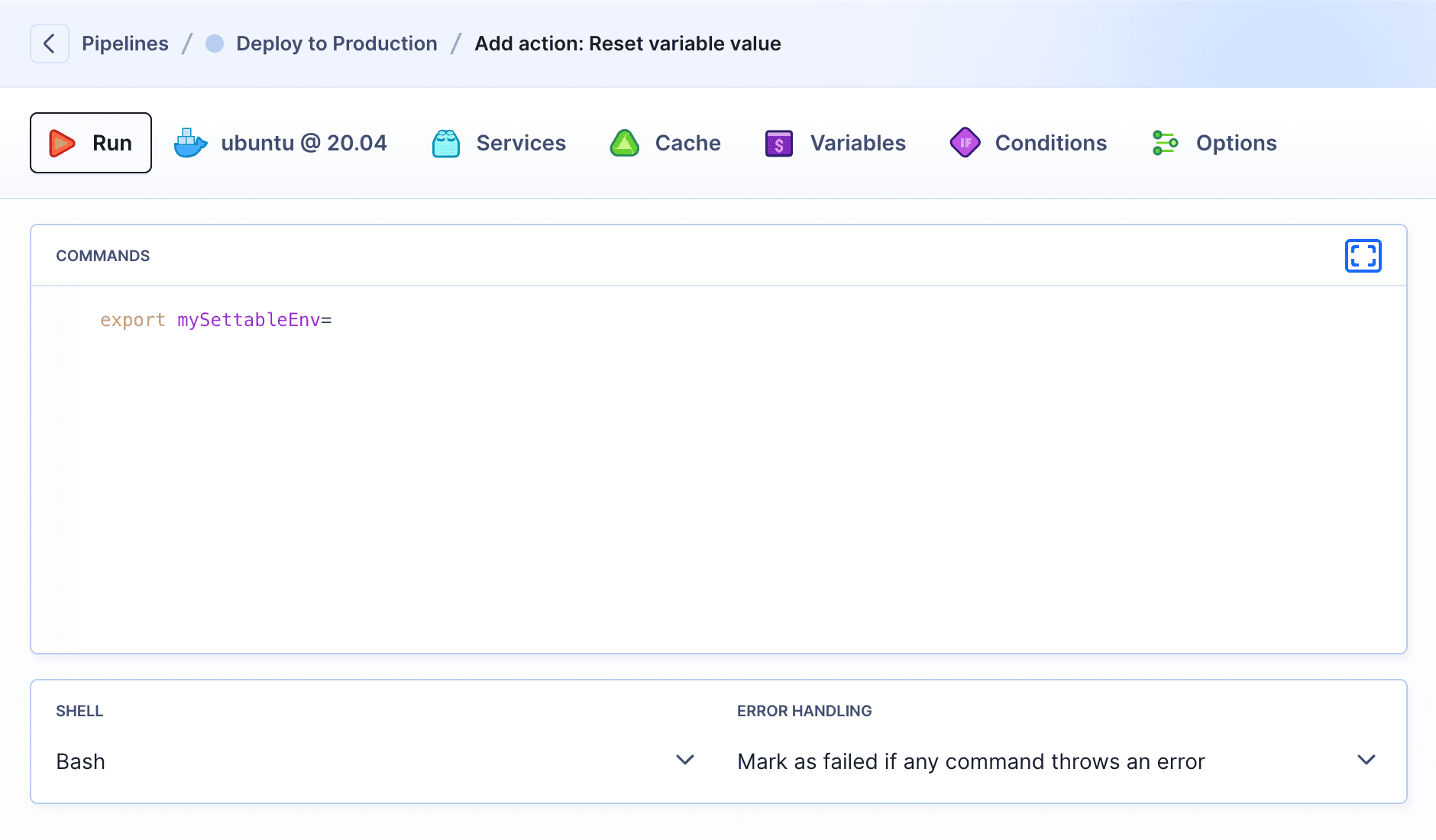
On pipeline start
You can parameterize your run using the Pass arguments action. It will pause the pipeline and wait for your input to proceed:
Image loading...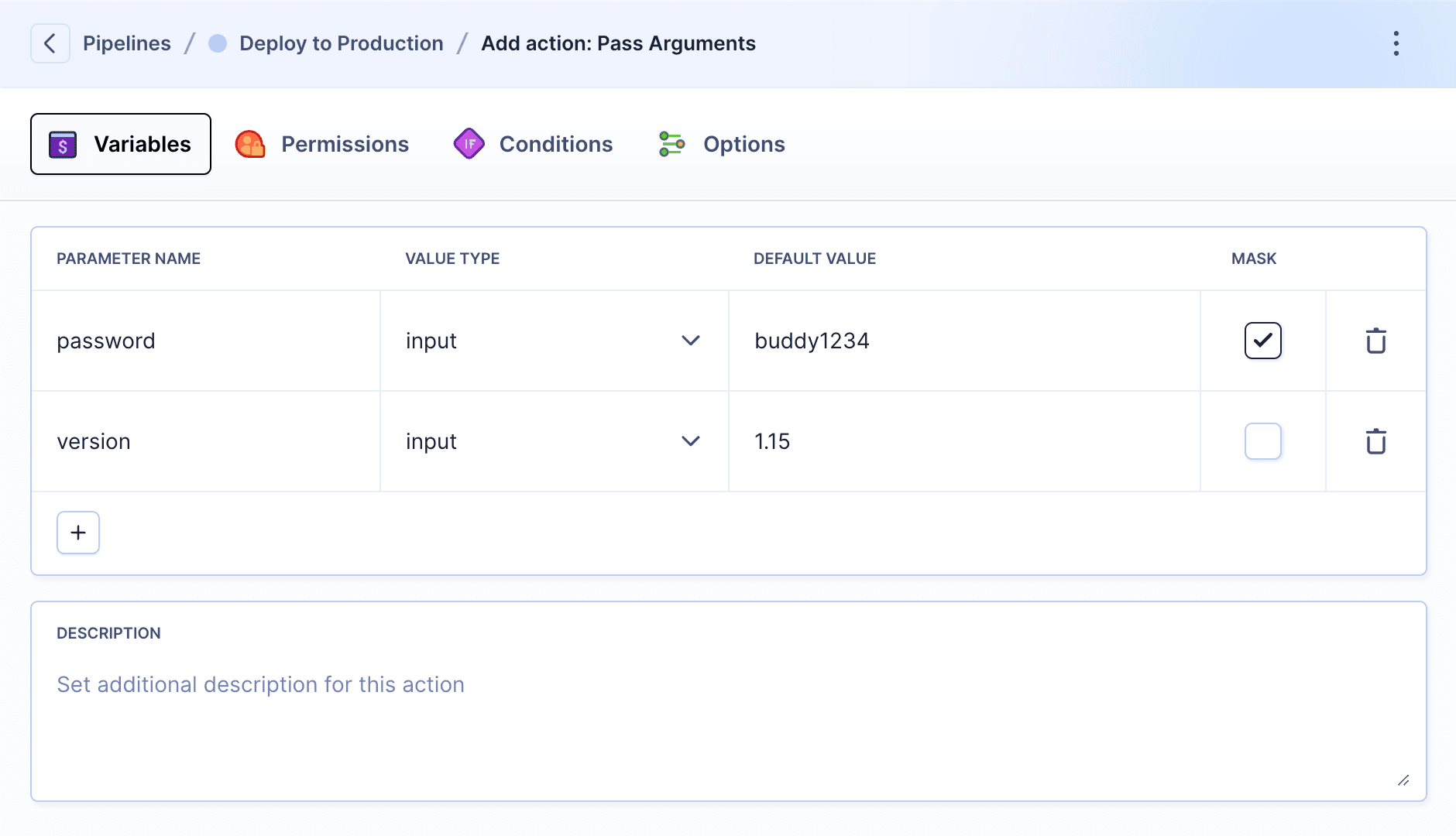
Output variables
In build actions, you can create variables with the OUTPUT_* prefix. These variables are automatically exported from the container and become available to subsequent actions in the pipeline.
bashexport OUTPUT_VERSION="1.2.3" export OUTPUT_STATUS="ok"$$
Example – passing version numbers and statuses between step:
yaml- pipeline: example_action_outputs name: Example – Action outputs (export) refs: - refs/heads/main events: - type: PUSH fail_on_prepare_env_warning: true actions: - action: Build App type: BUILD docker_image_name: buddy/localshell docker_image_tag: ubuntu_24.04 execute_commands: - VERSION=$(date +'%Y.%m.%d')-build-$BUDDY_RUN_ID - ./build.sh --version "$VERSION" - export OUTPUT_APP_VERSION="$VERSION" shell: BASH - action: Run tests type: BUILD docker_image_name: buddy/localshell docker_image_tag: ubuntu_24.04 execute_commands: - ./run-tests.sh --version "$OUTPUT_APP_VERSION" - ' export OUTPUT_TEST_STATUS="passed"' shell: BASH - action: Deploy type: BUILD docker_image_name: buddy/localshell docker_image_tag: ubuntu_24.04 execute_commands: - ./deploy.sh --version "$OUTPUT_APP_VERSION" - export OUTPUT_DEPLOY_ENV="staging" shell: BASH
Image loading...
How it works:
- Build App generates a version and exports OUTPUT_APP_VERSION (visible in the “Outputted Variables” section).
- Run tests uses this version and adds OUTPUT_TEST_STATUS (both variables are now available).
- Deploy uses the version and adds OUTPUT_DEPLOY_ENV (all three variables are now available).
Each action can see all previously exported variables in the “Outputted Variables” section and use them in its commands.
Last modified on Oct 28, 2025