CI/CD for Django
📚 Learn more about Django action features, integrations and alternatives.
With Buddy, you can create a pipeline that builds, tests, and deploys Django applications on a push to Git. The configuration is super simple and takes 10 to 15 minutes.
Image loading...
1. Create a new project
Go to Projects and click Create new project. Select your Git hosting provider (Buddy, GitHub, Bitbucket, GitLab, or Private Server) and enter your project name.
Image loading...
2. Add a new pipeline
Navigate to Pipelines and click New pipeline. In the form, configure the following:
- Name - Enter a descriptive name for your pipeline (e.g., "Deploy to production")
- ID - Optional identifier for the pipeline
- CPU - Select architecture: x64 or ARM64
- Resources per pipeline run - Choose resource allocation (default: Workspace default)
- Definition Location - Optionally check "Store configuration in a Git repository" to use YAML files
Click Add pipeline to create it.
Image loading...
3. Configure workflow: contexts and triggers
After creating the pipeline, go to the Workflow tab to configure:
Image loading...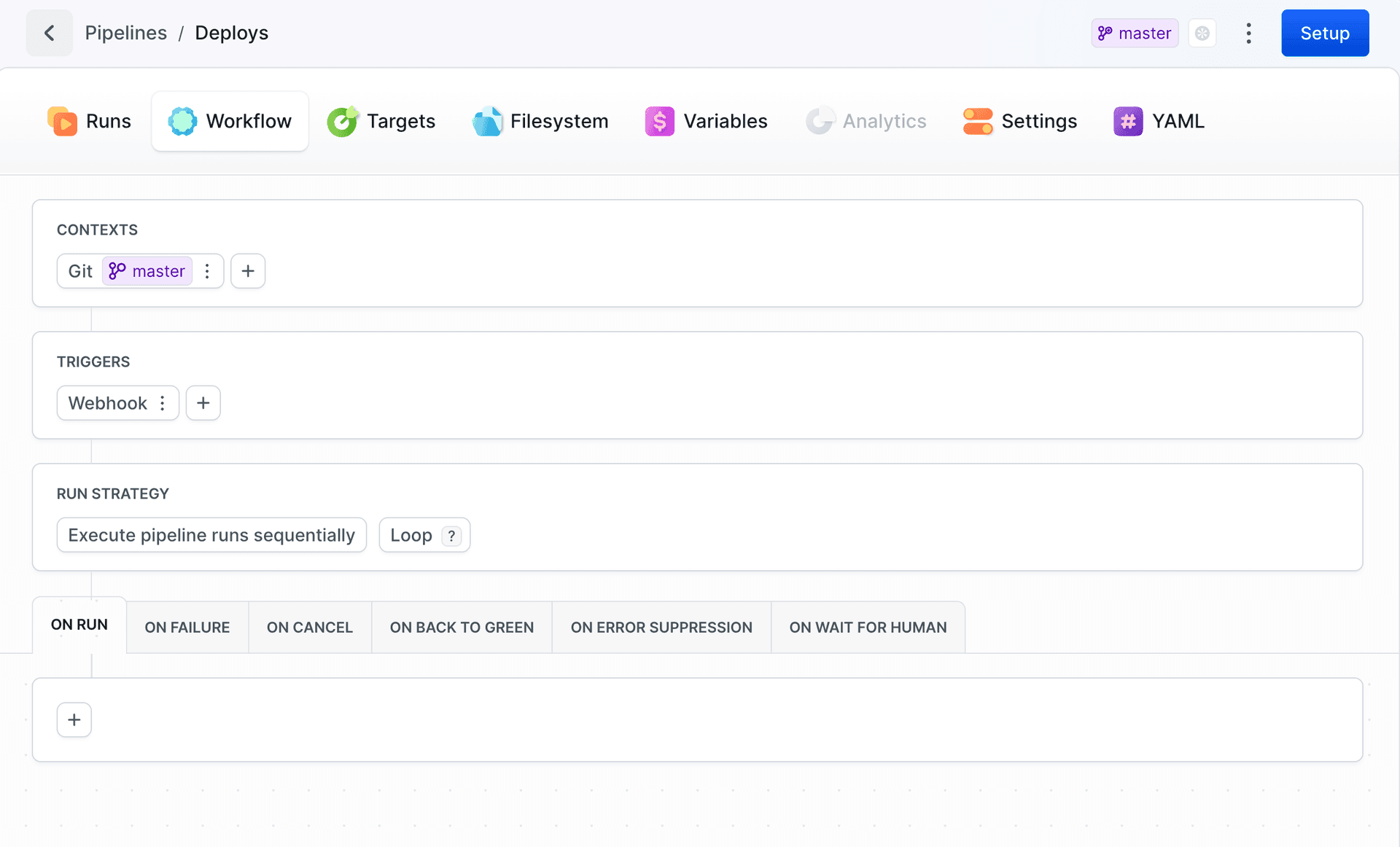
Contexts - Click
+to add Git branch/tag context or Environment. See Contexts.Triggers - Click
+to add Git events, Schedule, or Webhook. See Workflow Configuration.
4. Add actions
Buddy lets you choose from dozens of predefined actions. In this example, we'll add 4 actions that will perform the following tasks:
- Download dependencies and run unit tests
- Compile assets with Gulp
- Upload code to server together with compiled assets
- Send notification to Slack
4.1 Build your Django application
Look up and click Django on the action list to add it to the pipeline:
Image loading...
The Run tab lets you determine the commands to execute. The default commands are:
bashpip install -r requirements.txt python manage.py test$$
Image loading...
3.1.2 Python version
You can change the version of Python and install missing packages & tools in the runtime environment tab:
Image loading...
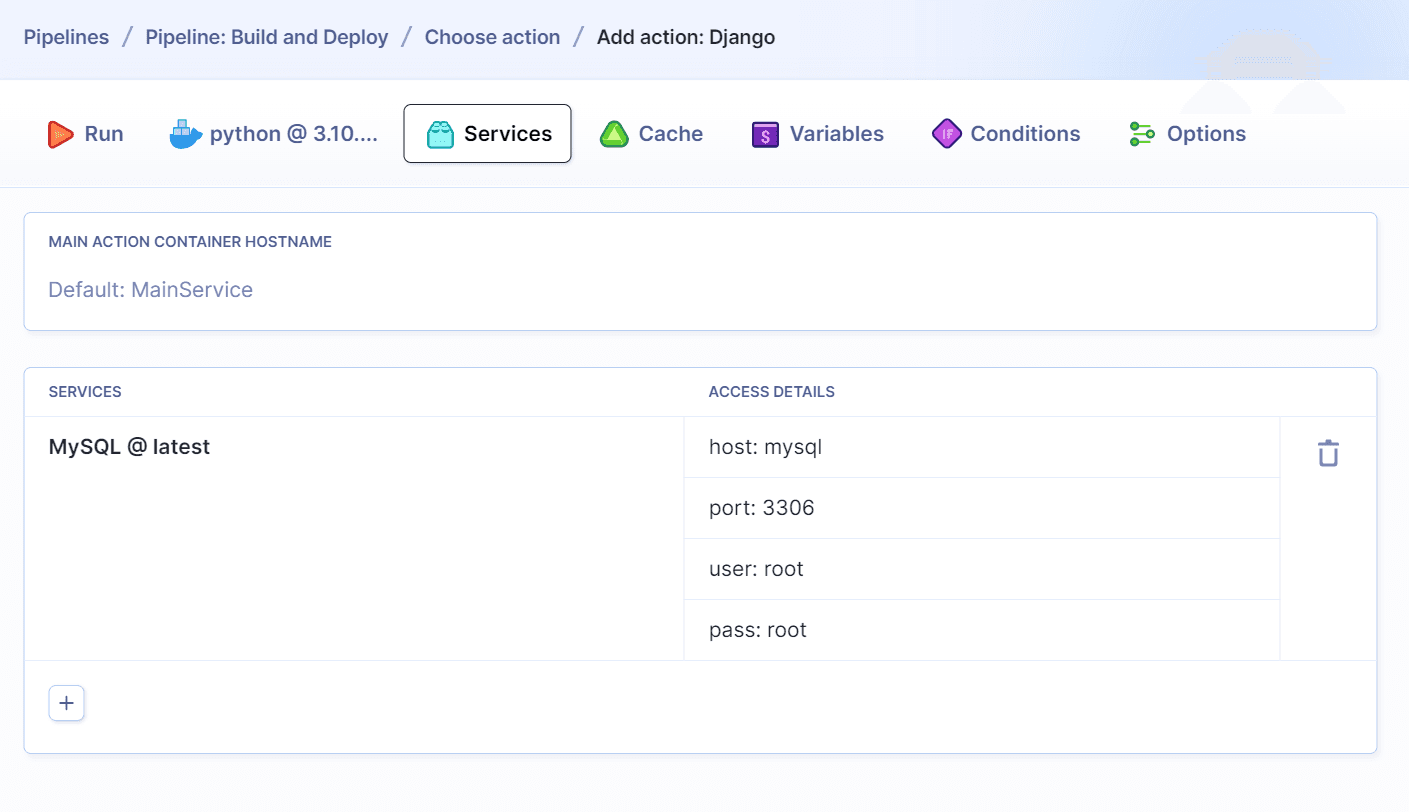
4.2 Run Gulp tasks
The next step is adding the Gulp action that will compile your assets and minify the code. To add a Gulp action, switch the tab to the Stacks section. You can find Gulp under Build Tools & Task Runners.
Image loading...
4.3 Deploy application to the server
The compiled application needs to be uploaded to the server. Head to the Deploy tab and select your upload action (Transfer in our case, where you can choose SFTP Target):
Image loading...
When adding the action you can choose what and where should be uploaded:
Image loading...
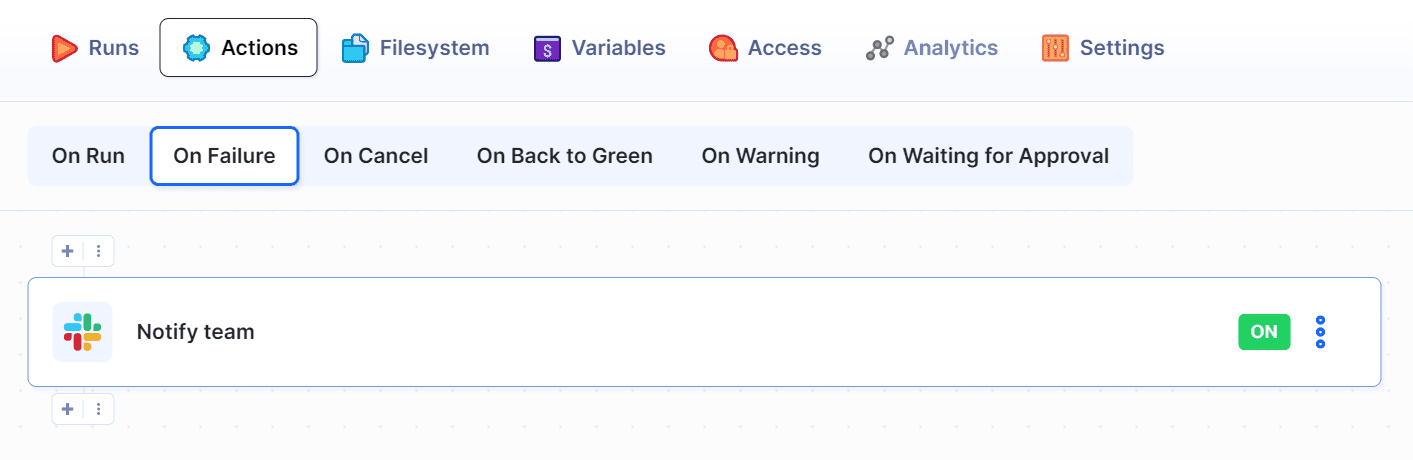
4.4 Send notification to Slack
You can configure Buddy to send your team a message after the deployment. In this example we'll use Slack:
Image loading...
5. Summary
Congratulations! You have just automated your entire delivery process. Make a push to the selected branch and watch Buddy fetch, build, and deploy your project. With Continuous Delivery applied, you can now focus on what's really important: developing awesome apps!
Last modified on Nov 20, 2025