Build Docker Image
Do more with Build Docker Image
Buddy CI/CD allows you to instantly implement Build Docker Image with 100+ ready to use actions to automate your development and build better apps faster.
Use Build Docker Image in Buddy CI/CDDo more with Build Docker Image
Buddy CI/CD allows you to instantly implement Build Docker Image with 100+ ready to use actions to automate your development and build better apps faster.
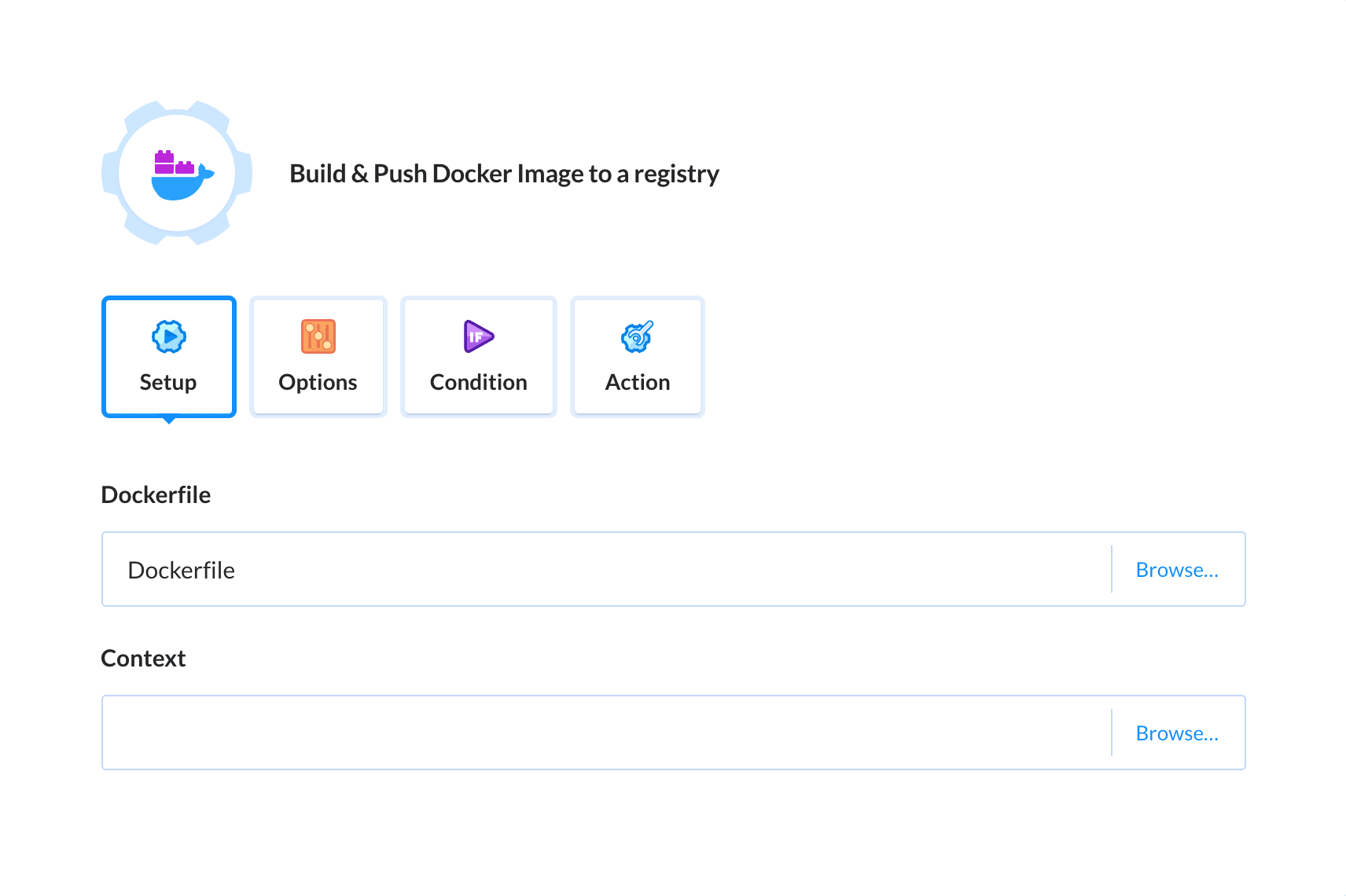
Use Build Docker Image in Buddy CI/CDThis action builds Docker image using Dockerfile. It’s also possible to use this action to push a built image to a Docker registry.
The action runs Docker build command in a context of a pipeline filesystem. If details to a private Docker registry are provided in the action's Options, the connection to the registry is established before the Docker build command is executed.
Buddy allows you to instantly connect Build Docker Image with 100+ actions to automate your development and build better apps faster.
Connect Build Docker Image to 100+ dev toolsBuild Actions
Google Cloud Platform
Build Actions
Amazon Web Services
Deploy to IaaS/PaaS
Deploy to IaaS/PaaS
Google Cloud Platform
DevOps
Amazon Web Services
Amazon Web Services
Amazon Web Services
Google Cloud Platform
Setup
Build Actions
Git Hosting Services
Performance & App Monitoring
DigitalOcean
DigitalOcean
DigitalOcean
DigitalOcean
Amazon Web Services
Amazon Web Services
Google Cloud Platform
Google Cloud Platform
Build Actions
Performance & App Monitoring
Google Cloud Platform
Google Cloud Platform
Google Cloud Platform
DevOps
Performance & App Monitoring
DevOps
Build Tools & Task Runners
Amazon Web Services
Amazon Web Services
Performance & App Monitoring
Performance & App Monitoring
Notifications
Code Quality & Review
Kubernetes
Kubernetes
Kubernetes
Performance & App Monitoring
Kubernetes
Download
Performance & App Monitoring
Uptime Monitoring
Virtual Machine