Create an Environment
Creating an environment helps organize and manage applications at different stages of the software lifecycle.
How to create an environment?
Navigate to the project you wish to create an environment in and select Environments. Click New Environment to begin environment configuration.
Image loading...
Click New Environment to begin environment configuration.
Image loading...
Environment configuration
Name ID - The name generates a unique identifier (
ID), which can be manually edited to match your workflow. You can also select an icon from the dropdown.Scope - Choose the scope of the environment:
WorkspaceorProject.Base-only (Optional) - Enable "Use as base-only environment" to make this environment serve as a foundation for other environments.
Base Environments (Optional) - Select parent environments that this environment should inherit configuration from.
Tags (Optional) - Add tags to organize your environments.
Public URL (Optional) - Provide the app URL, e.g.
https://dev.myproduct.com.
Image loading...
Once done, you can now see your environment on the list.
Image loading...
Base Environments
Base Environments allow you to create a hierarchy where one environment inherits configuration from another. When an environment has a specified base environment, it automatically inherits:
- Targets - deployment destinations (FTP, SFTP/SSH)
- Integrations - connected services and tools
- Files - environment filesystem files
- Variables - environment variables
Setting up base environments
To create a base environment that can be inherited by others, enable the Use as base-only environment checkbox in the BASE-ONLY section when creating or editing an environment.
Image loading...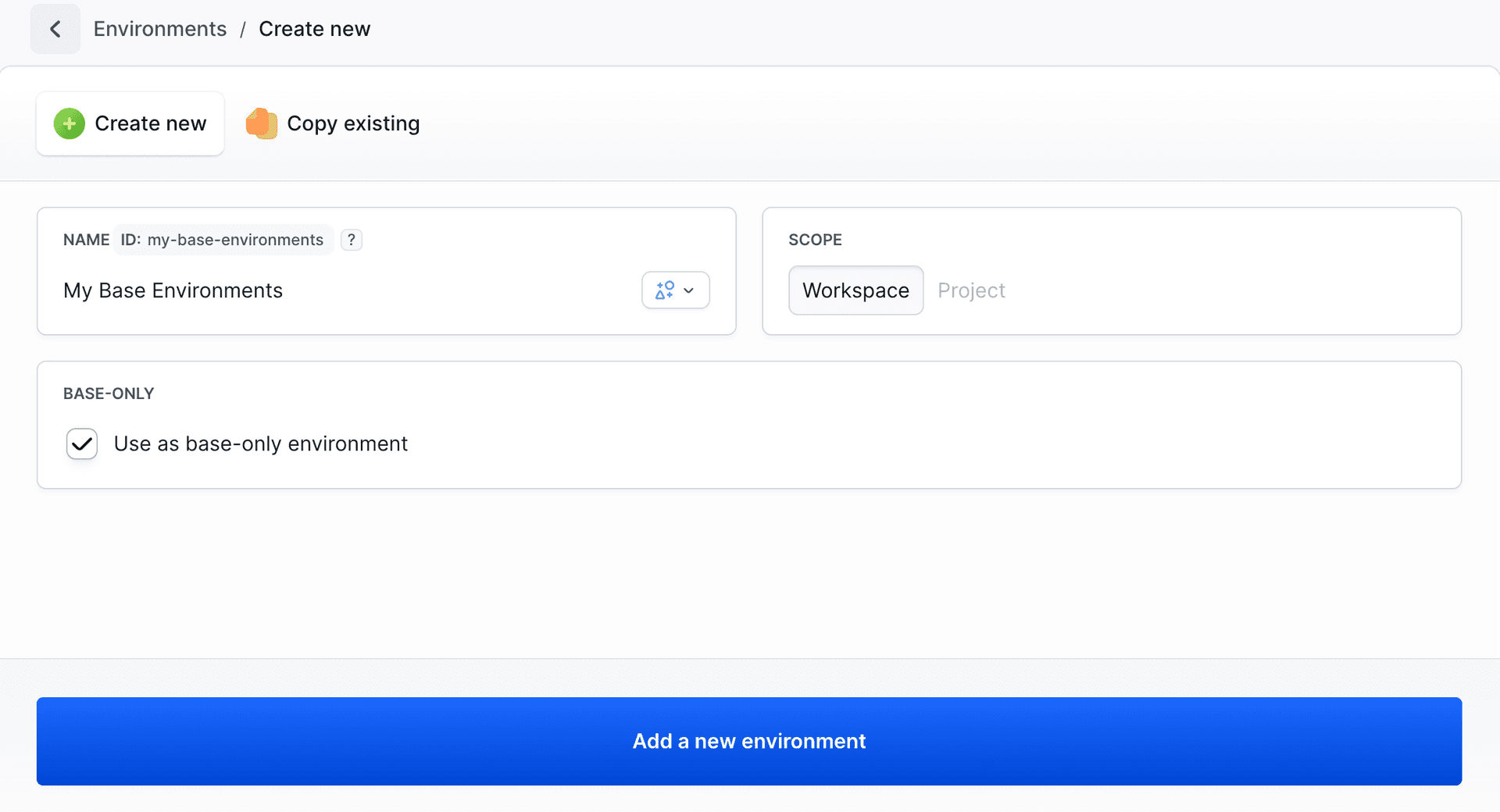
To inherit from existing base environments, select them in the BASE ENVIRONMENTS field. You can choose multiple base environments from the list.
Image loading...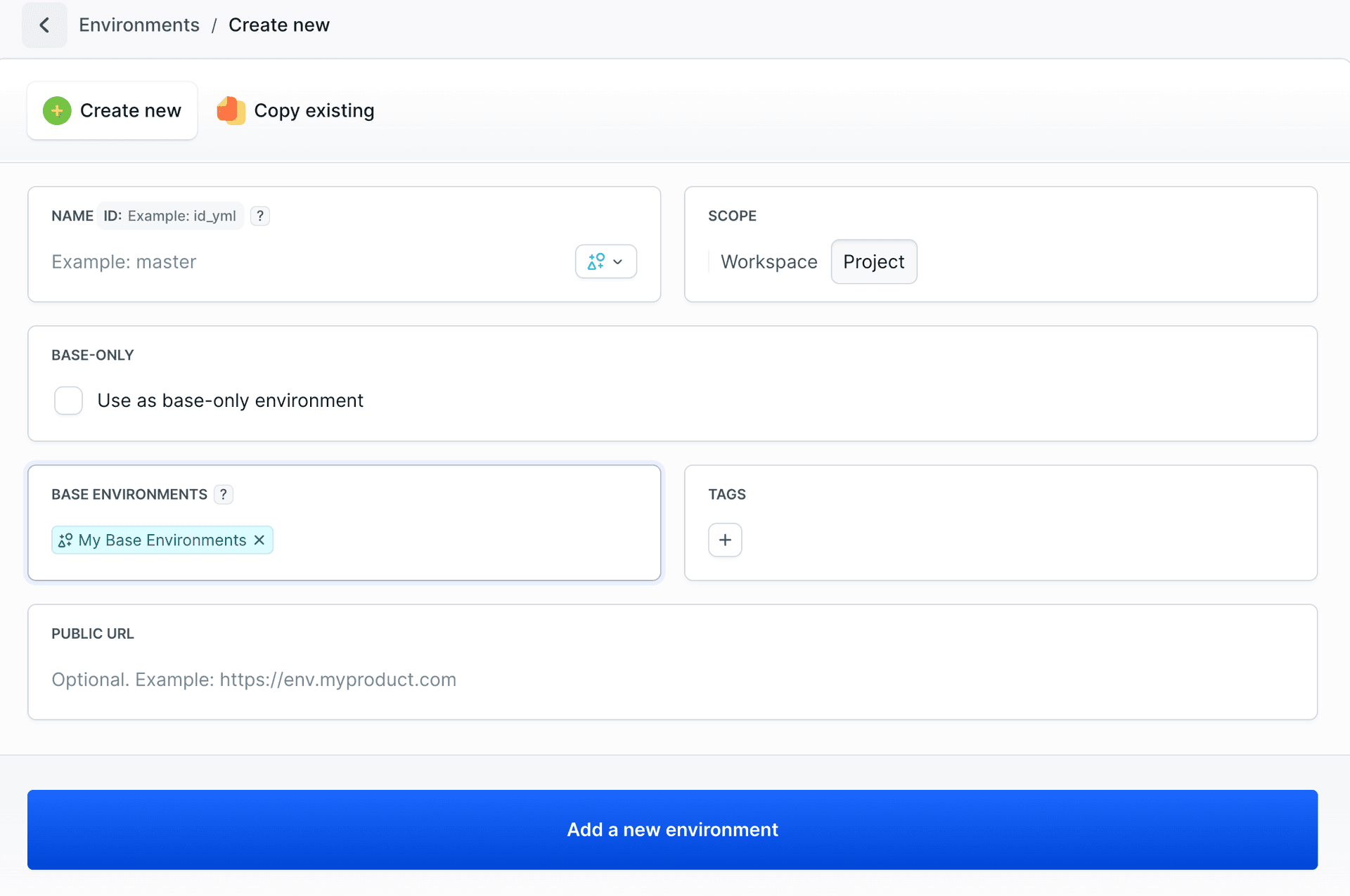
How inheritance works
- Multiple base environments - You can specify more than one base environment to inherit from.
- No chaining - An environment cannot be set as a base if it already has its own base environment.
- Inheritance order - Resources are inherited in the order base environments are defined, with the last base environment having the highest priority.
- Overriding - Targets/integrations with the same ID and variables/files with the same name will override objects from the base environment.
Use cases
Base environments are useful when you want to:
- Share common configuration across multiple environments (e.g., shared API keys, common deployment targets).
- Create environment templates that can be reused.
- Maintain consistency while allowing specific overrides per environment.
Assigning environment to pipelines
With the environments created, you can assign them to pipelines in the Contexts section of the pipeline settings by selecting Environment or Environment: Match by filters.
Image loading...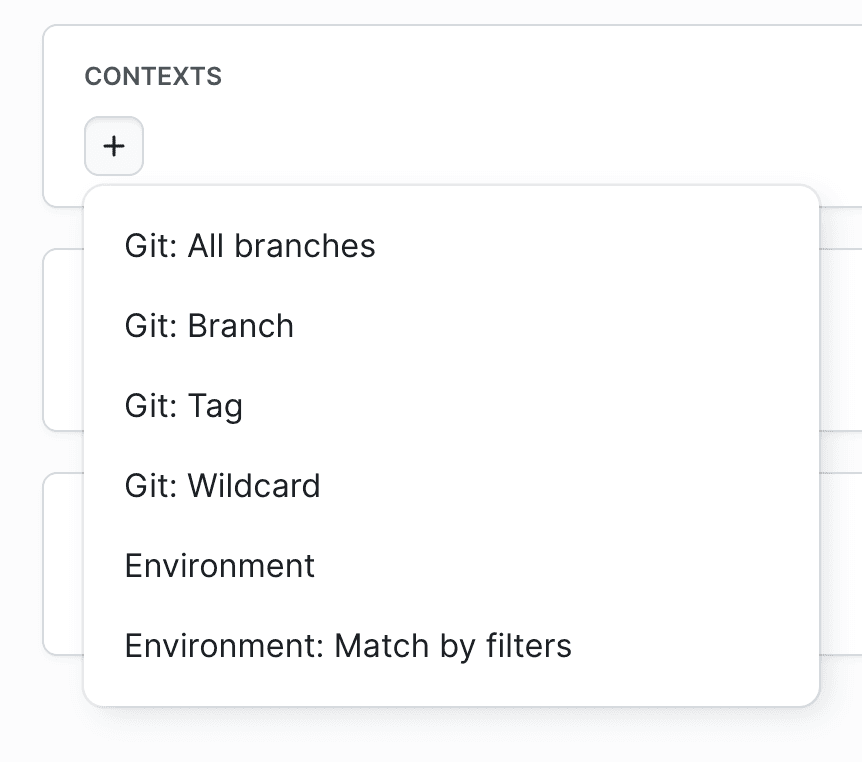
Matching filters Environments
You can filter the environments based on their ID, Scope or Tags. That way, instead of manually assigning each environment, you can automate the process.
All criteria (ID, SCOPE, TAGS) are applied simultaneously using the logical AND operator. This means that an environment must meet all conditions to be selected. However, it's important to note that multiple contexts with different filters can be added to a pipeline. So, even though the AND operator is used within a single filter, you can include different variations.
Image loading...
ID filtering
Environment ID is unique, unlike the Name field (Environment name), which can be arbitrary and changed for organizational purposes. It is recommended to use the ID when matching environments in the Match Filters section.
In the ID field, you can use regular expressions (regex) to easily match environments with a specific naming pattern.
Examples:
*stage- matches all environments that ID end withstage.stage_*- matches all environments that ID begin withstage_.*- matches all available environments regardless of the name.
Tag filtering
Tags enable the organization and search of environments based on assigned tags. Regex does not work in the Tags field - you must select the exact tag name from those previously used.
Image loading...
Create an Environment using REST API
Besides the user interface, environments can also be created using Environment REST API, allowing for quick and automated deployment.
Last modified on Dec 12, 2025